Loss of urine is a common problem that can affect people of all ages, but it is particularly common elderly. It can be a light form, such as losing a few drops when sneezing or laughing, up to heavier forms where someone the control over the bladder function Fully loses. Although the subject is sometimes considered taboo, there are many opportunities to tackle urine loss and to improve the quality of life.

The first step in experiencing urine loss is to understand the underlying causes, which range from physical changes, such as After pregnancy, to certain medical conditions. Various treatments are possible, ranging from pelvic floor therapy to medication. A professional diagnosis is crucial to find appropriate treatment and not to deteriorate the situation unnecessarily.
Self -management also plays an important role in dealing with urine loss. This can, for example, consist of training the pelvic floor muscles, change in diet and keeping a pee diary. It is important to remember that both conservative measures and surgical options are available. For personalized advice, it is advisable to consult a general practitioner.
What is loss of urine?

Loss of urine, also known as incontinence, refers to the involuntary outflow of urine. It is a common problem that can affect people of all ages, but is more common in the elderly.
Types of urine loss
- Stress incontinence: This type of urine loss occurs when pressure (stress) is exerted on the bladder, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing or lifting.
- Incontinence: Here one experiences a sudden, intense urge to pee, followed by immediately loss of urine.
- Overflow incontinence: This happens when the bladder is not fully emptied, resulting in frequent dripping.
- Functional incontinence: With this type of urine loss, an individual cannot reach the toilet on time due to physical or mental barriers.
Causes of urine loss
- Physical: Pregnancy, delivery and menopause in women; prostate problems in men.
- Medication: Some medicines can have incontinence as a side effect.
- Neurological disorders: Diseases such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's can influence the nerves that regulate the bladder.
- Lifestyle factors: Excessive caffeine use and alcohol can irritate the bladder.
For a clear overview of the various causes that can contribute to urine loss, consult Unintentional loss of urine (urinary incontinence) in the elderly and Loss of urine - from causes to treatment.
Urine loss diagnosis

A correct diagnosis is crucial with urine loss to determine the correct treatment. Doctors look at the specific symptoms and conduct medical research to determine the nature and causes of incontinence.
Recognize symptoms
Patients with loss of urine often report various symptoms. Ranging from light urine loss in pressure -increasing moments such as coughing or sneezing, up to a sudden and fierce To pee. Recognizing these symptoms is a first step in the direction of a diagnosis.
Medical
A medical Is essential for an accurate diagnosis. This can include a physical examination, looking at the physical condition of the pelvic floor muscles. In addition, tests such as urine analyzes or bladder function tests can be performed to gain insight into the causes of loss of urine.
Treatments for loss of urine

When tackling urine loss, various treatment options are available, depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. It is crucial to consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis and treatment plan.
Lifestyle adjustments
Lifestyle adjustments can be a first step in the treatment of urine loss. Examples of this are Reducing caffeine intake, tackle overweight and stop smoking, which can reduce the unintentionally loss of urine.
Pelvic floor exercises
Pelvic floor exercises, also known as cone exercises, reinforce the muscles that support the bladder. Regular training can help with both exercise incontinence as urgent incontinence.
Medication
Depending on the type of incontinence, medicines can be prescribed to reduce the symptoms. These drugs can bladder muscles relaxed Or strengthen the muscles around the Urethra.
Surgical procedures
In some cases a surgical procedure may be necessary, for example if other treatments are not effective. Operations can vary from it Place a sling To inject bulk agents in the urethra.
Practical tips for daily activities
Small changes in daily activities can make a big difference in dealing with urine loss. The following tips can help to control urine loss in daily life.
Protective products
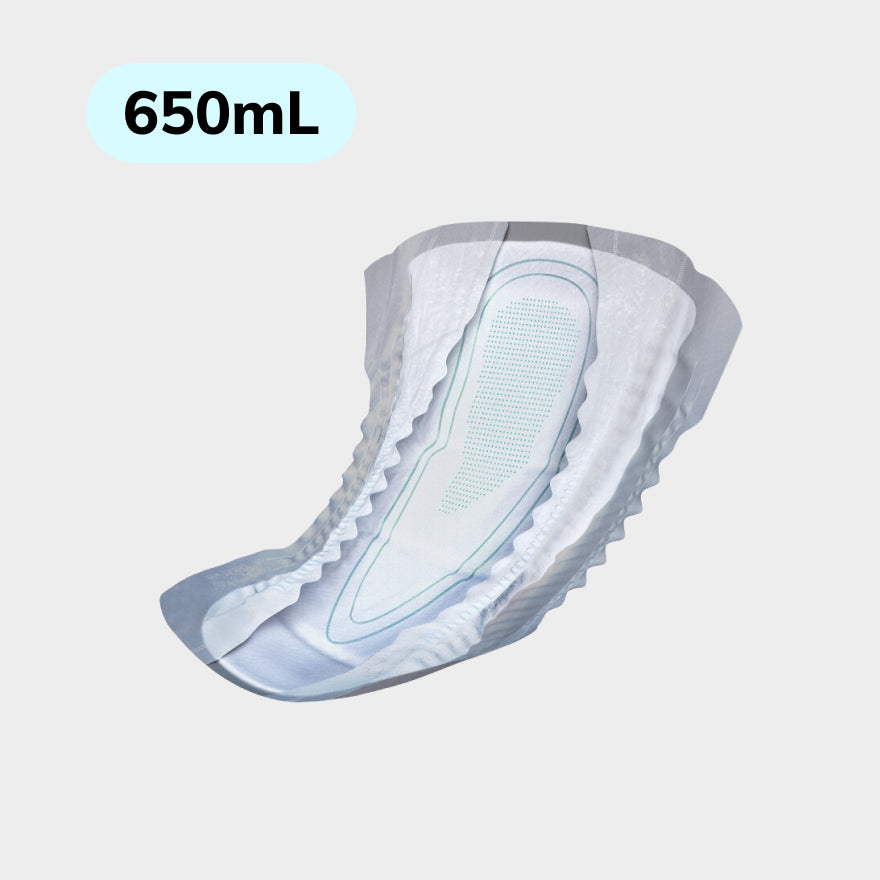
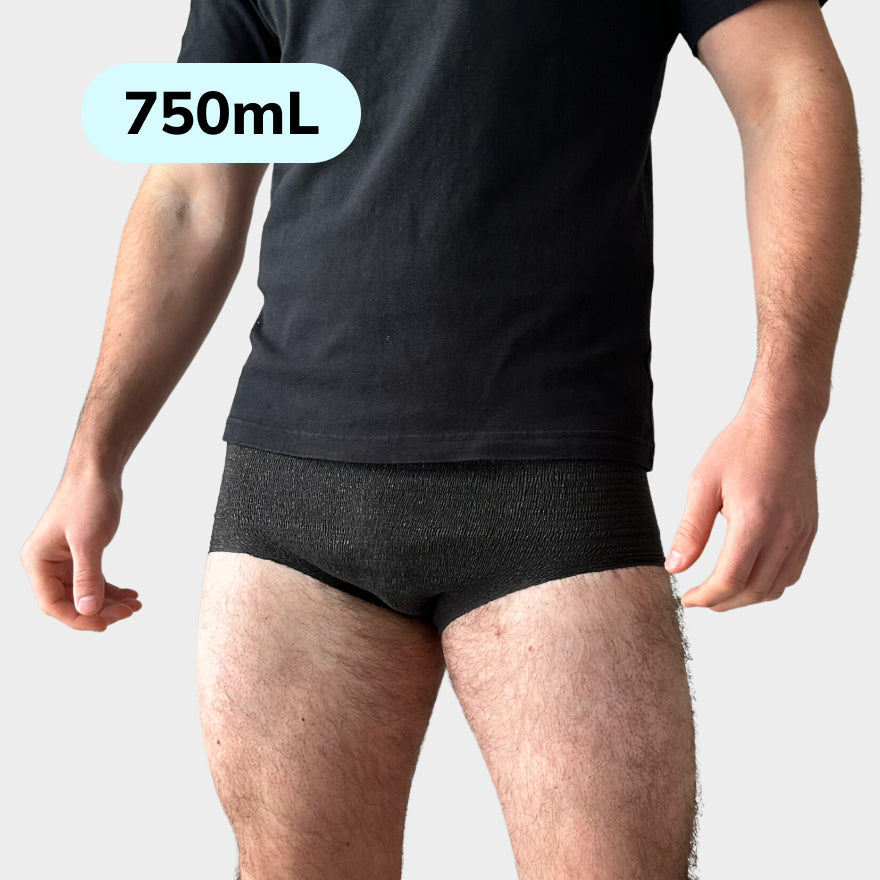
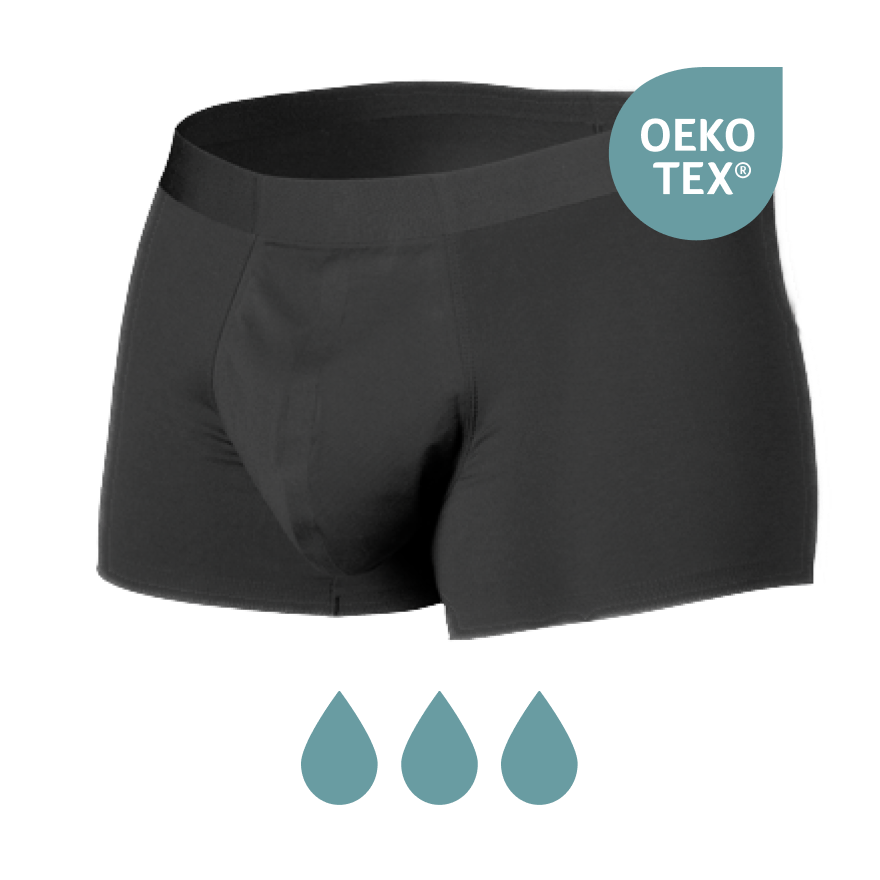
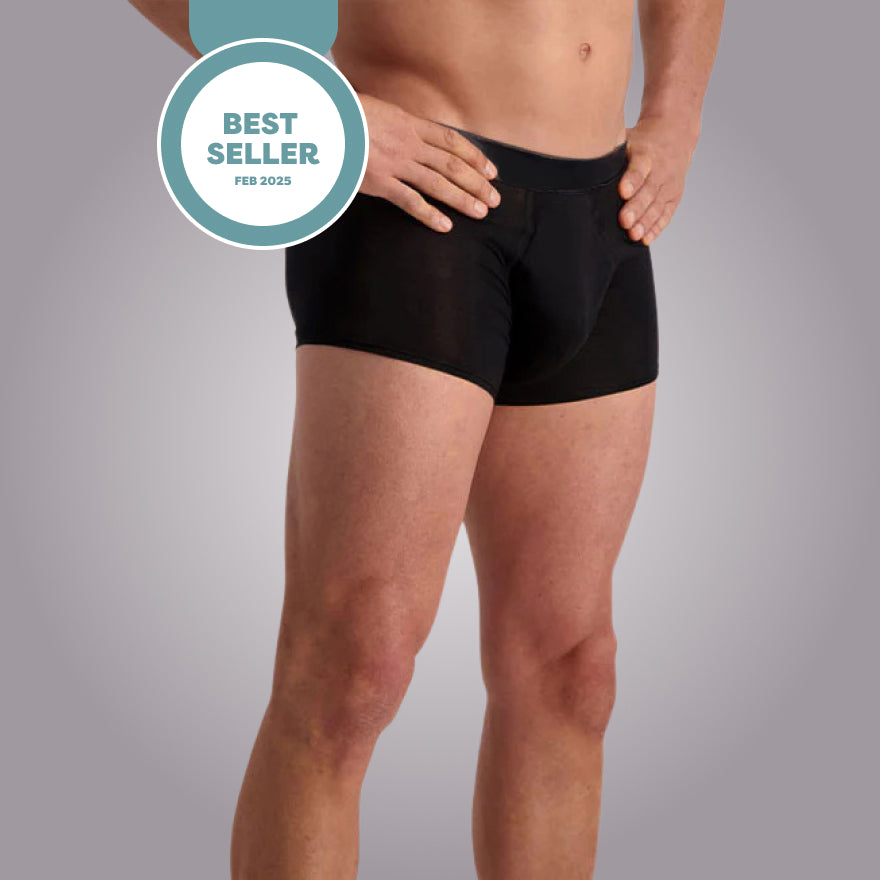
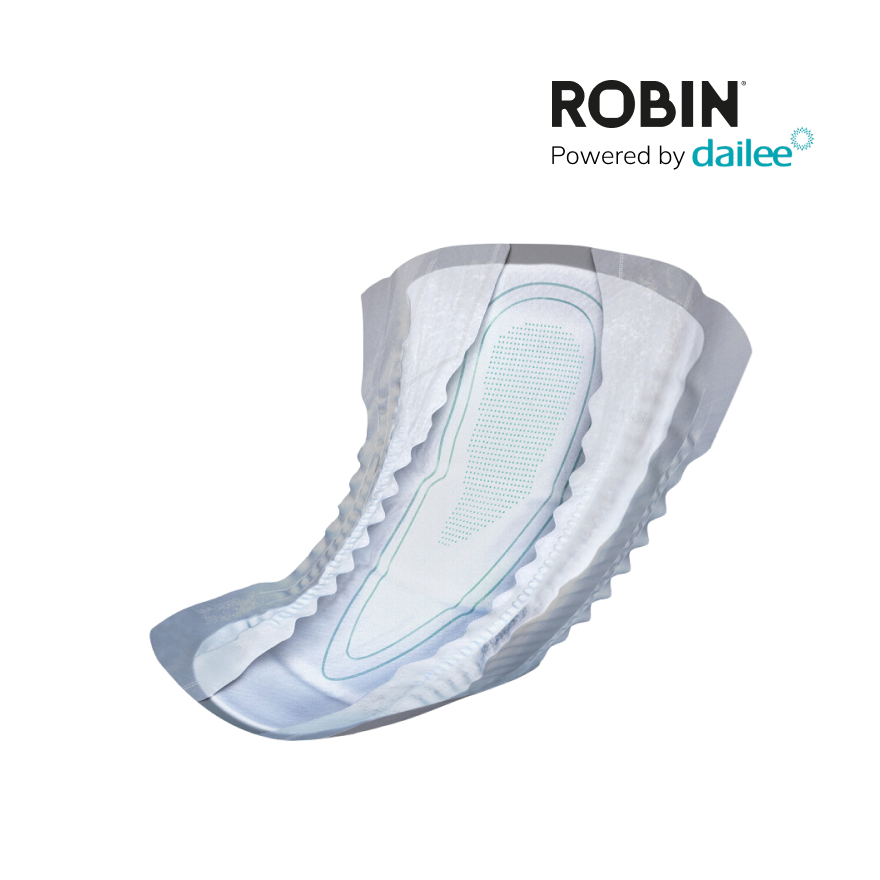
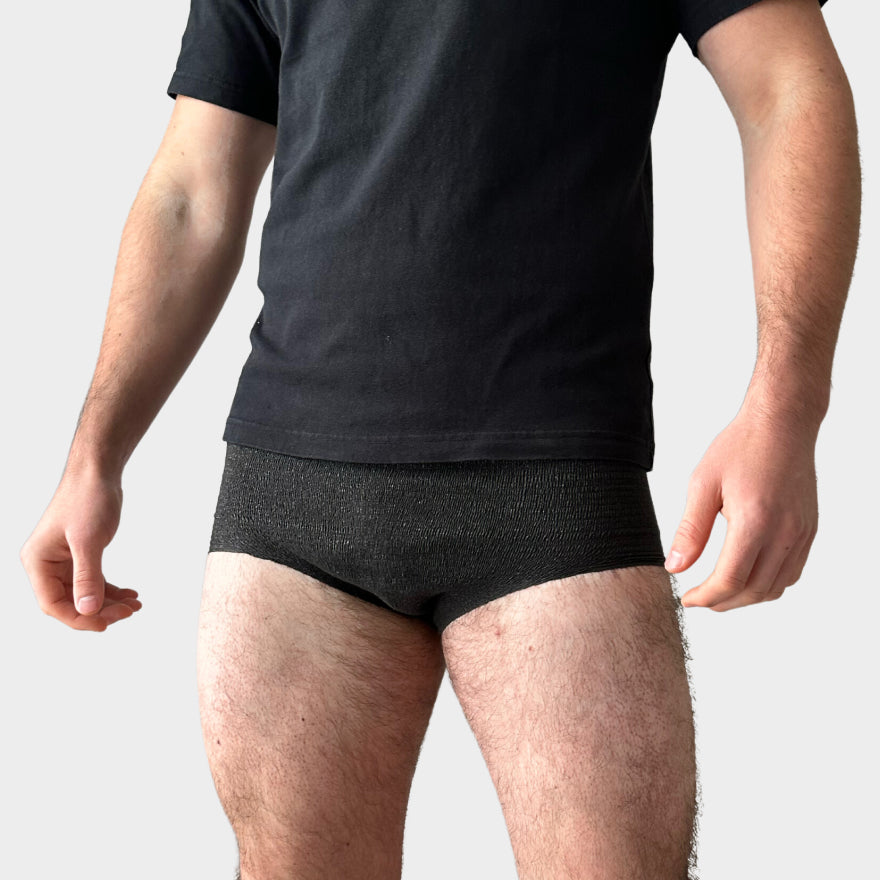
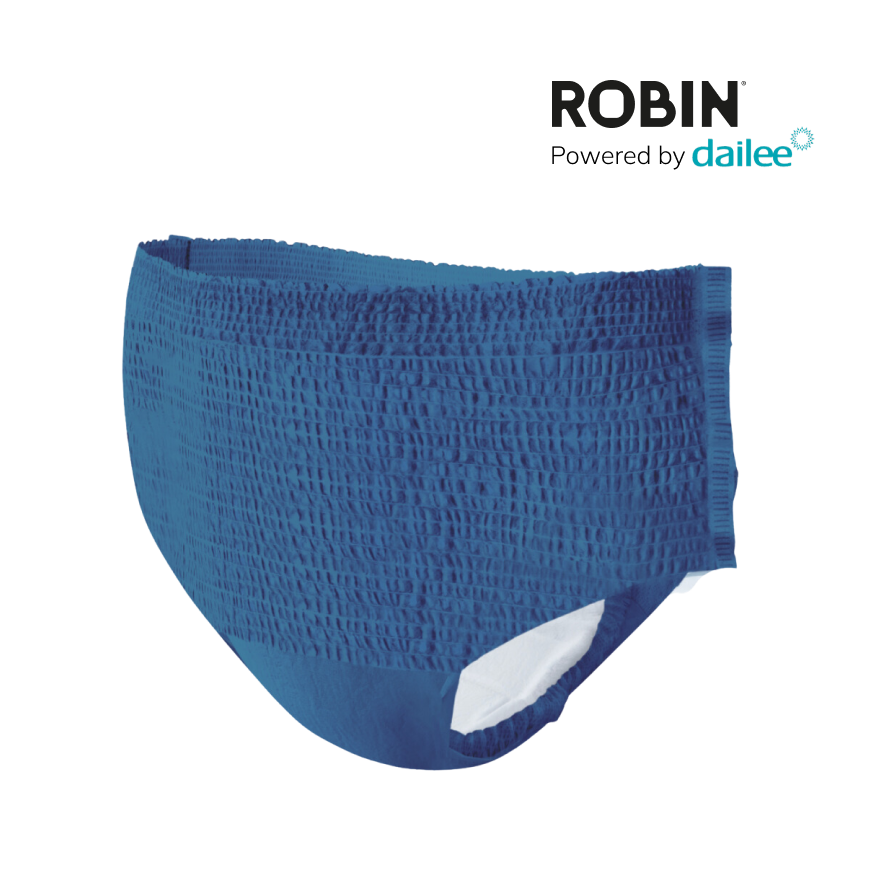
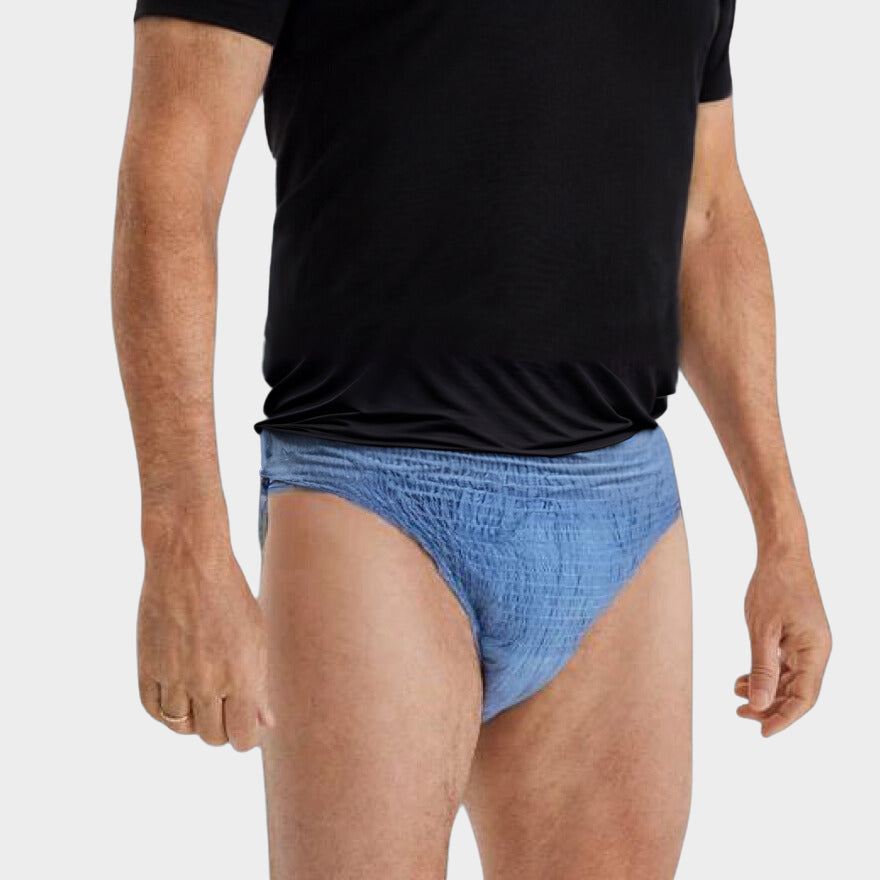
Using the correct Protective products Is essential. There are various types of incontinence material available, such as panty liners, connections and special underwear that can be worn discreetly. These products are designed to absorb moisture well and to neutralize odors. It is important to choose the right product that fits the degree of urine loss.
Adjust toilet habits
Adjust toilet habits Can also help with controlling urine loss. One can try to go to the toilet less often to train the bladder or, on the contrary, to prevent accidents. It is also advisable to take the time during the toilet visit, so that the bladder is completely emptied. Leaning forward while urinating can help with this.
Dietary advice
Dietary advice Play a significant role in urine loss. It is recommended to:
- Enough water to drink: This helps prevent bacterial growth in the bladder.
- Fiber -rich food: This stimulates digestion and helps prevent blockage and associated bladder pressure.
It is also wise to reduce or avoid food and drinks that can irritate, such as caffeine, alcohol and spicy food.
Emotional support

In addition to physical discomfort, urine loss can have a significant emotional impact. It is essential to tackle not only the physical aspect, but also the emotional challenges that accompany it.
Dealing with the condition
Accepting urine loss as a medical condition is an important first step in controlling it. Openness about the situation can lead to better understanding and support of family and friends. It is important that the affected person strives for an active lifestyle and is not restrained by fear or shame.
Supporting groups and counseling
Participation in supporting groups Can offer personal experiences and advice that bring lighting. Specialist counseling Can also be useful in processing feelings and developing coping strategies. Professionals can offer individual support that is tailored to personal needs.
Prevention of loss of urine

Prevention of urine loss is aimed at reducing the risk of incontinence and may consist of various measures. It is essential to limit risk factors and to take preventive steps.
Preventive measures
Prevention can include training the pelvic floor muscles, which can improve bladder control. It is recommended to perform pelvic floor exercises that can be learned from a pelvic floor physiotherapist. You can also regulate moisture intake, although it is important to keep drinking enough to prevent dehydration. Caffeinated drinks, alcohol and carbonated drinks may be limited, since they can irritate the bladder.
Limit risk factors
Various lifestyle choices and health conditions can increase the risk of loss of urine. Maintaining a healthy weight is important, since overweight can put extra pressure on the bladder. One can also be careful with certain drugs that have diuretic or muscle relaxing effects because they can worsen the situation. Stopping smoking is also an essential step, because smoking increases the chance of coughing, what can cause stress incontinence.