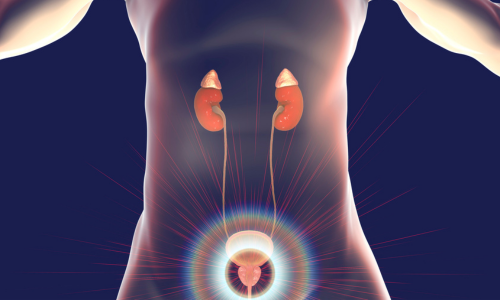
Prostate problems are common in men, especially as they age. The prostate, a walnut-sized gland, is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. This gland plays a vital role in the male urogenital system, but when problems occur, men can experience a range of symptoms. These symptoms range from urinary problems to more serious conditions, such as prostate cancer. 
Often prostate problems start with urinary complaints, such as having to urinate more often, difficulty holding or starting urination, a weak stream or the feeling that the bladder is not completely empty. In some cases prostate problems can also cause pain in the pelvic area. As men get older, it is important to be aware of changes in their urination pattern and discuss these with a doctor in a timely manner.
Diagnosis and treatment for prostate problems can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. A urologist may perform several tests to identify the cause of your symptoms. Treatment options may be conservative, such as medications and lifestyle changes, or more invasive, such as surgical procedures. Education about symptoms and treatment options is essential, such as the information provided at HealthNet , where you can learn more about how to recognize and treat prostate problems.
Causes of Prostate Problems
Prostate problems can have a variety of causes, including benign prostate enlargement, inflammation, and prostate cancer. Each of these conditions has specific causes and risk factors.
BPH - Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that often occurs in men over the age of fifty. It is a natural consequence of aging and is caused by a change in hormone balance, which leads to an increase in prostate tissue. Symptoms of BPH include frequent urination , difficulty urinating, and a weak urine stream. More information about BPH and its treatment can be found at Andros Clinics .
Prostatitis
Prostatitis refers to an inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be acute or chronic. Causes range from bacterial infections to stress and certain lifestyle factors. Acute prostatitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection and is often accompanied by severe pain and urinary problems. Chronic prostatitis, on the other hand, can cause a more persistent inflammation with less intense symptoms.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a serious condition and one of the most common cancers in men. The cause of prostate cancer is not fully understood, but genetics, age, race, and diet are considered major risk factors. Education about the symptoms and treatment options for prostate cancer is crucial and information can be found on websites such as Health Net and other reputable medical sources.
Symptoms of Prostate Disease

Prostate diseases are accompanied by various symptoms that can affect daily life. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
General Symptoms
Prostate problems can manifest in a variety of symptoms that many men experience when dealing with these conditions. These often include problems with urination such as:
- Having to urinate frequently and frequently, especially at night.
- Difficulty urinating or a slower urine stream.
- Dribbling after urination.
- The feeling that the bladder is not completely empty.
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating.
Some men also complain of pain between the scrotum and rectum , which may be an indication of inflammation, as shown in some health information .
Symptoms Specific to Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer can be subtle and sometimes have no specific symptoms. As the cancer progresses, specific symptoms may occur, such as:
- Blood in the urine or semen.
- Pain in the lower back, hips or upper legs.
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue.
- Erectile dysfunction.
These symptoms may also be indicative of other prostate problems, but persistent or severe symptoms should always be evaluated by a doctor for further evaluation and treatment .
Diagnosis and Investigations

Diagnosis and tests are crucial to diagnosing prostate problems, such as prostate cancer. Several methods are used to ensure accuracy.
PSA test
The PSA test measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. Elevated PSA levels can be an indication of prostate cancer, but this requires further analysis by professionals, as other factors can also increase PSA.
Rectal Examination
During a Rectal Toucher, the doctor feels the prostate with a finger through the rectum. Abnormalities in size or structure can indicate problems that require additional examination.
Biopsy
If previous tests indicate prostate cancer, a biopsy may be performed. In this procedure, the urologist takes a small piece of tissue from the prostate to examine for cancer cells.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans are used to map the presence, size and spread of prostate tumors. These techniques are essential for determining the stage of the cancer.
Treatments and Interventions

Treatments for prostate problems depend on the specific condition and range from medication to surgery. Each treatment aims to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Drug Treatment
For an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer, medications such as alpha blockers and hormone therapy may be prescribed to control prostate growth and reduce symptoms. Medications such as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can help shrink the prostate.
Surgical Options
Surgical interventions such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) may be considered for severe urinary problems. Other methods, such as laser therapy , offer alternatives with potentially lower risk of complications.
Radiotherapy
Individual treatments such as external beam radiation or brachytherapy, in which radioactive seeds are placed in the prostate, are used for prostate cancer that is limited to the prostate.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to traditional treatments, patients may also opt for supportive alternative therapies. These can range from herbal supplements to lifestyle changes, although it is important to be aware of the scientific evidence and consult a physician.
Frequently Asked Questions

Prostate problems can be accompanied by a variety of symptoms and there are various treatment options. Understanding these aspects is essential for recognizing and treating prostate complaints.
How can you recognize prostate problems yourself?
Men can recognize prostate problems themselves if, for example, they have difficulty urinating or experience a weakened urine stream. Frequently having to go to the toilet, especially at night, can also be an indication. For more details, one can consult 11 practical questions about prostate problems .
What are the ways to treat prostate problems?
Treatment for prostate problems ranges from medication and lifestyle changes to surgical interventions. The choice depends on the severity and cause of the problems. Prostate problems? Read 6 frequently asked questions for insight into the treatment options.
What is the connection between prostate problems and erectile dysfunction?
There is a link between prostate problems and erectile dysfunction; the prostate can affect sexual function. For example, an enlarged prostate can put pressure on the urethra, which can cause problems with erection. More information is available at Prostate Problems? Don't Wait Too Long .
What are the early signs of prostate disease?
The first signs of prostate disease may include difficulty starting the urine stream, a weak stream, or the feeling that the bladder is not completely empty after urination. See Prostate problems: these are the signs for a more detailed discussion of these signs.
What indicates an inflammation of the prostate?
Symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen, genital area or lower back, pain when urinating or ejaculating and fever may indicate an inflammation of the prostate, also called prostatitis.
What symptoms may indicate prostate cancer?
Symptoms that may indicate prostate cancer include persistent problems with urination, blood in the urine or semen, and bone pain. There is essential information available in the context of prostate cancer at I have prostate cancer .