Did you know that your pelvic floor muscles are superheroes? They support your bladder, bowels, and uterus, and play a crucial role in regulating urination. But sometimes, even superheroes need a little workout! That’s where pelvic floor exercises come in. Also known as Kegel exercises, these exercises help strengthen those muscles.
Why is that important? Well, a strong pelvic floor can help reduce or even prevent unwanted urine leakage, also known as incontinence. And you know what’s great? These exercises work for both men and women!
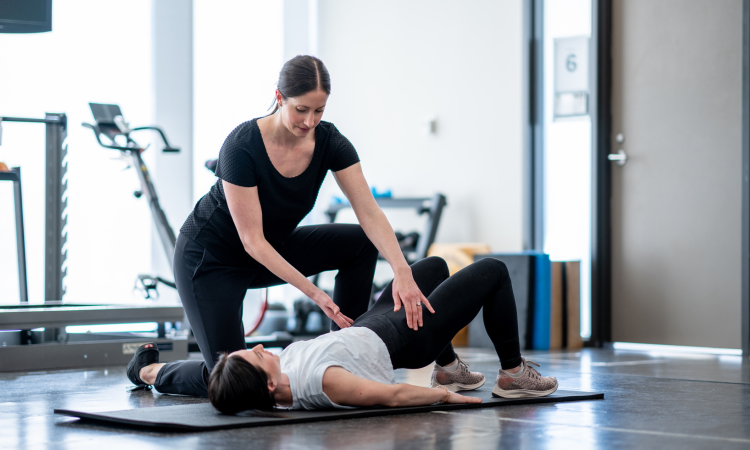
But as with any workout, consistency is key. It is important to perform the exercises regularly and correctly for the best results. Sometimes it can help to get advice from a physiotherapist to make sure you are performing the exercises correctly.
3 Effective Pelvic Floor Exercises to Combat Urinary Incontinence
Pelvic floor exercises are essential for strengthening the muscles that help control urinary incontinence. These exercises can be done daily to strengthen the pelvic floor and improve control.
1. Kegel exercises
Kegel exercises, also known as pelvic floor muscle exercises, focus on tightening and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles. Step-by-step approach:
- Identify the correct muscles by tensing the muscles used to stop urination.
- Tighten these muscles, hold for three to five seconds, and then relax.
- Frequency: Repeat this cycle ten to fifteen times per session.
- Number of sessions per day: Three times.
2. Bridge exercises
Bridge exercises not only strengthen the pelvic floor muscles but also the gluteal and lower back muscles. Execution:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Lift the pelvis up to form a straight line from the knees to the shoulders.
- Duration: Hold the bridge for five to ten seconds.
- Repetitions: Perform ten times per session.
3. Squat Exercises
Squats are effective for increasing pelvic floor strength. Procedure:
- Stand with your feet slightly wider than hip-width apart.
- Bend your knees as if you were going to sit on a chair, keeping your back straight.
- Depth: Make sure the hips do not drop lower than the knees.
- Number: Work up to three sets of ten reps.
These general pelvic floor exercises can make a significant contribution to the prevention and treatment of incontinence. It is important to perform the exercises regularly and correctly. If necessary, one can ask for guidance from a physiotherapist.
Importance of Pelvic Floor Training for Incontinence
Pelvic floor training is an essential component in the treatment of incontinence. The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that support the bladder, bowel, and, in women, the uterus. Incontinence, or the involuntary loss of urine, can result from weakened or damaged pelvic floor muscles.
Benefits of pelvic floor training:
- Improving muscle strength: Regular exercise can strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor, which contributes to better bladder control.
- Prevention of worsening: Without training, muscles can weaken further, which can increase incontinence.
- Reduction of symptoms: Many people experience a significant reduction in incontinence complaints after targeted pelvic floor training.
It is important to perform pelvic floor exercises correctly. Incorrect techniques can lead to minimal improvement or even worsening of incontinence symptoms.
Important exercises:
- Kegel exercises: Tightening and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles.
- Bridge exercises: Raising the hips while lying on your back can also strengthen the pelvic floor.
Under the guidance of a health care provider, patients can learn how to perform these exercises correctly. It is advisable to consult a specialized physiotherapist for a personalized exercise program.
Consistency in pelvic floor exercises is critical to results. Patients must commit to a routine to achieve the best results. They must also be aware of proper urination and defecation techniques to support progress.
Exercises for Women

Women can perform specific pelvic floor exercises to reduce incontinence. These exercises are effective after pregnancy and for older women.
Exercises After Pregnancy
After pregnancy, it is important for women to strengthen their pelvic floor. Kegel exercises are an effective method:
- Contract your pelvic floor muscles as if you were stopping urination.
- Hold this tension for five seconds and then relax.
Women should repeat this exercise several times a day, with the aim of gradually increasing the duration of muscle contraction.
Exercises for Older Women
For older women, pelvic floor exercises are crucial to maintain muscle strength. The following is a suitable exercise:
-
Bridge exercise:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Lift your pelvis while contracting your abdominal muscles.
- Hold this for three seconds and slowly lower back down.
Consistency in this exercise helps increase bladder control.
Pelvic Floor Anatomy and Functions

The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and ligaments that close off the bottom of the pelvis. These muscles are crucial for supporting the pelvic organs, such as the bladder, bowel, and for women, the uterus.
Main functions of the pelvic floor:
- Support : The pelvic floor muscles keep the pelvic organs in place.
- Sphincter control : They help regulate urination and bowel movements.
- Sexual function : They are involved in sexual sensation and orgasmic function.
- Stability : Together with the abdominal and back muscles they form a 'muscular corset' for the pelvis.
The anatomical structure :
- Bee women the pelvic floor is wider and less high than in men, which is partly due to its function in the childbirth process.
- Bee men the pelvic floor mainly provides support to the bladder and intestines.
Pelvic floor muscles include the levator ani (composed of the pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus, and puborectalis) and the coccygeus. The pelvic floor muscles work together by contracting and relaxing, thereby performing the above functions.
The integrity of the pelvic floor is essential for preventing incontinence. When these muscles are weakened, such as after childbirth or through aging, it can lead to urinary incontinence or other pelvic dysfunction. Pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen these muscles and restore or improve control of the pelvic organs.
Exercises for Men
Pelvic floor exercises can help men regain bladder control after prostate surgery.
Exercises After Prostate Surgery
After prostate surgery, men can perform specific pelvic floor exercises to help reduce incontinence. Regularly contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles helps strengthen these muscles and improve bladder control. It is essential to perform these exercises correctly and to be patient; results may take some time to appear.
Daily Routine:
- Start by identifying the pelvic floor muscles by stopping the flow of urine.
- Contraction : Hold the pelvic floor muscles contracted for 5-10 seconds.
- Relaxation : Relax the muscles for the same period.
- Repeat this 10-15 times per session.
- Perform 3 sessions per day.
Following this exercise routine consistently will help improve muscle strength and urinary control. A physical therapist can provide guidance for a personalized exercise program.
Progressive Pelvic Floor Resistance Training
Progressive resistance training is an effective method to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and combat incontinence. The principle is based on gradually increasing the resistance during exercises to build muscle strength.
Beginning with Basic Exercises: The training starts with basic exercises such as Kegel exercises , where one contracts, holds and then relaxes the pelvic floor muscles. One starts by contracting the muscles for a few seconds and gradually increases this.
- Short and often: Short sessions several times a day.
- Duration and intensity: Gradual increase in the duration and intensity of contractions.
| To soften | Duration of tension | Break |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | 3-5 seconds | 10 sec |
| 3-4 | 6-10 seconds | 10 sec |
| 5+ | 10+ seconds | 5 sec |
Use of Equipment: As one becomes stronger, one can use equipment such as cone weights or vaginal cone balls to increase resistance.
Stay Consistent: Regularity in training is crucial. Consistent exercise ensures progressive improvement in muscle condition and helps in controlling incontinence.
It is recommended that these exercises are performed under the supervision of a physiotherapist to ensure that they are performed correctly and safely. This will also help to tailor the training program to individual needs and progress.
Breathing Techniques and Pelvic Floor
The connection between breathing techniques and the pelvic floor is crucial in addressing incontinence problems. The importance of diaphragm and pelvic floor synchronization is often emphasized.
- Diaphragm: This is the main muscle of breathing. When a person inhales, the diaphragm moves down and the pelvic floor muscles relax. When exhaling, the diaphragm moves up and the pelvic floor muscles contract.
- Pelvic floor: A series of muscles and ligaments that form the lower support layer of the pelvis.
Well-coordinated breathing supports pelvic floor function and can subconsciously contribute to reducing incontinence symptoms by improving muscle control.
Step-by-step exercises:
Inhalation:
- Feel the relaxation: As you inhale, feel the pelvic floor gently lower and relax.
- Direct the breath: By directing the breath towards the abdomen, more space can be created for pelvic floor relaxation.
Exhalation:
- Subtle contraction: With the exhalation, the pelvic floor gently pulls up and the muscles contract.
- Don't force: The emphasis is on natural movement without exaggerating.
| Breathing phase | Pelvic floor activity |
|---|---|
| Inhalation | Relaxation |
| Exhalation | Tension |
Instructors recommend practicing these techniques regularly to achieve optimal results in treating incontinence. They emphasize consistency and patience in strengthening the pelvic floor through breathing exercises.
Mindfulness and relaxation exercises for the pelvic floor
Mindfulness and relaxation exercises can be crucial in managing incontinence, as they help to reduce stress and improve pelvic floor function. By becoming aware of the body and calming the mind, one can gain more control over the pelvic floor muscles.
Pelvic floor awareness:
- Focusing: Begin by focusing your attention on your pelvic floor. Consciously feel how these muscles contract and relax.
- Breathing: Focus on deep, slow breaths that help relax the pelvic floor as you exhale.
Relaxation techniques:
-
Progressive muscle relaxation:
- Consciously tense each muscle group, including those in the pelvic floor, and then relax them.
- Start at the feet and work your way up to create awareness of the entire body.
-
Visualization:
- Visualize tension leaving the body with each exhalation.
- Imagine your pelvic floor muscles feeling stronger and more controlled after each session.
Mindfulness meditation:
- Take time daily for mindfulness meditation by focusing on the present and letting go of any distracting thoughts.
- The exercise should be done regularly for optimal effect on pelvic floor control.
The combination of these exercises promotes the mind-body connection, which is essential for managing incontinence. It is recommended to integrate these exercises into your daily routine for best results.
Technology Aids and Apps

To support pelvic floor exercises for incontinence, various technological aids and applications are available. These tools are designed to guide users and optimize their exercise routines.
Pelvic Floor Training Apps :
- Pelvic Floor Trainer : This app provides guided exercises and tracks progress.
- Tät : An app specifically developed for women, providing information and exercises.
Biofeedback devices :
- Elvie Trainer : This wearable device connects to an app and provides real-time biofeedback.
- kGoal : An interactive pelvic floor trainer that works with an app and provides feedback on exercise performance.
Wearables :
Users can also use wearables designed to track how often and how correctly pelvic floor exercises are performed.
Electronic Stimulation :
For those who have difficulty activating their pelvic floor muscles, electronic stimulation devices can be helpful. These devices help contract and relax the muscles.
| Device | Description |
|---|---|
| Elvie Trainer | Pelvic floor trainer with app for exercises and biofeedback |
| kGoal | Measures pressure and provides vibration feedback during exercises |
| This app | Educational tool with exercises for women |
The use of these technologies can improve the effectiveness of exercises and motivate users to consistently work on their pelvic floor strength. However, one should always consult a medical professional before using new therapeutic devices.
Nutritional Tips for a Strong Pelvic Floor

A balanced diet contributes to a healthy pelvic floor. Certain foods can promote the strength and elasticity of the pelvic floor muscles.
-
Water : Adequate hydration is essential. At least 1.5 to 2 liters of water per day helps prevent urinary tract infections, which is important for maintaining a strong pelvic floor.
-
Fiber : Foods rich in fiber help with regular bowel movements, which reduces pressure on the pelvic floor. Examples of fiber-rich foods include:
- Fruits, such as apples and pears
- Vegetables, such as broccoli and carrots
- Whole grains, such as oats and quinoa
-
Healthy Fats : Omega-3 fatty acids, found in oily fish and flaxseed, can reduce inflammation and are important for muscle health.
-
Protein : Proteins are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Sources of high-quality protein include:
- Lean meats, such as chicken breast
- Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas
- Dairy products, such as yogurt and cottage cheese
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Water, herbal tea | Hydration, Urinary Tract Health |
| Fibres | Vegetables, fruits, whole grains | Regular bowel movements |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Fatty fish, linseed | Anti-inflammatory |
| Proteins | Chicken, legumes, dairy products | Muscle building |
Limit your consumption of caffeine and alcohol as they can irritate the bladder. It is also advisable to avoid heavy and spicy foods as these can cause digestive problems that put extra pressure on the pelvic floor.
Common Questions and Myths About Pelvic Floor Exercises
Q: Do pelvic floor exercises work for everyone with incontinence?
Answer: Pelvic floor exercises can be effective for many people with incontinence, but they do not work for everyone. The effectiveness depends on the cause and type of incontinence.
Question: Are pelvic floor exercises only for women?
Answer: No, both men and women can benefit from pelvic floor exercises to strengthen the muscles that support the bladder.
Myth: It is impossible to train your pelvic floor muscles incorrectly.
Fact: It is important to perform pelvic floor exercises correctly. Incorrect training can lead to more problems or a lack of improvement.
| Myths | Facts |
|---|---|
| You should do pelvic floor exercises continuously. | Regular exercise is important, but rest periods are also necessary for muscle recovery. |
| Incontinence is only an old age problem. | Although incontinence is more common in older people, it can affect individuals of any age. |
Q: How quickly do you see improvement?
Answer: This varies from person to person; some notice improvement within a few weeks, while for others it can take months.
For best results it is recommended to follow instructions from a qualified pelvic floor physiotherapist. They can adapt individual exercises and check for correct execution.