Introduction
Prostate stones, although less talked about, affect a significant number of men as they age. Studies have shown a prevalence of between 7% and 70%, indicating the need for further research. Despite their prevalence, many men are unaware of the potential impact of these stones on prostate health.
In this article we discuss the causes, development, symptoms and treatment options for prostate stones.
What are prostate stones?
Prostate stones are small deposits of calcium and phosphate that form in the prostate gland. They can vary in size and number. Although they are often harmless, they can sometimes cause serious symptoms.
Causes of prostate stones
There are several factors that contribute to the formation of prostate stones. One of the main causes is chronic prostatitis , a long-term inflammation of the prostate. Other factors may include:
- Age : Older men are at higher risk. Prostatitis can occur at a younger age. However, as men get older and the prostate grows in size, the chance of developing prostate stones also increases. Almost every man over the age of 60-65 develops one or more of these stones in the prostate.
- Nutrition : A diet rich in calcium may help.
- Hydration : Insufficient fluid intake may increase the risk.
- Urinary retention : Problems with complete emptying of the bladder.
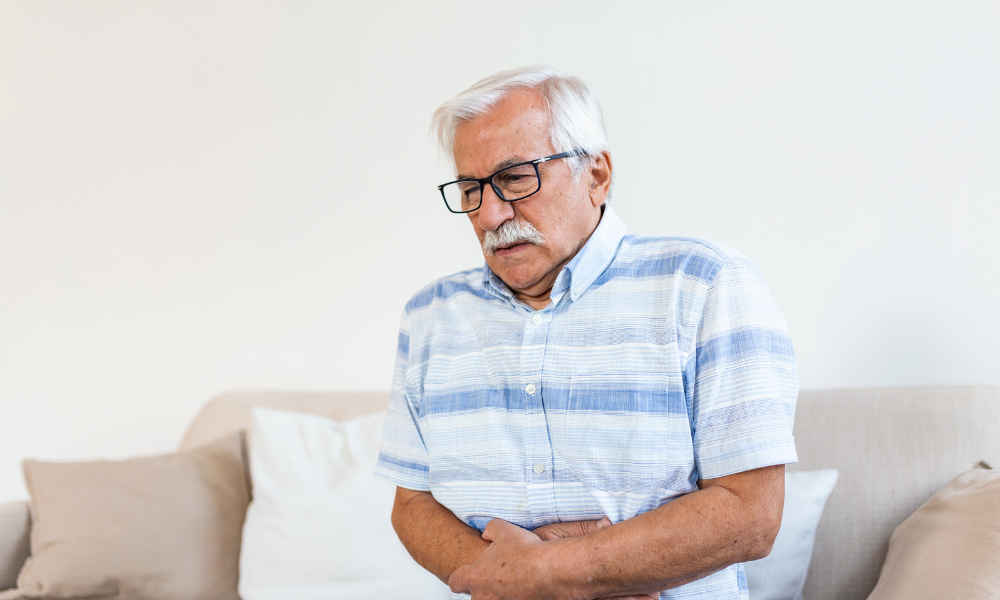
Symptoms of prostate stones
Not everyone with prostate stones experiences symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen or lower back
- Difficulty urinating or a weak urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain during ejaculation
However, many of these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions such as urinary tract infections or incontinence. If you have these symptoms, see your doctor immediately for a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of prostate stones
Diagnosing prostate stones often begins with a visit to your primary care physician. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and may recommend additional tests, such as:
- Urine test : To rule out infections.
- Ultrasound : For a detailed image of the prostate.
- CT scan or MRI : For a more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Prostate Stones
Treatment for prostate stones depends on the severity of symptoms and the size of the stones. Possible treatments include:
- Medication : To relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation.
- Hydration : Drinking plenty of water can help flush small stones.
- Surgery : In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the stones.
- Minimally invasive procedures : Such as laser treatment to break up stones.
Prevention of prostate stones
Preventing prostate stones is not always possible, but there are some steps men can take to reduce their risk:
- Healthy Diet : Avoid foods high in calcium and eat a balanced diet.
- Stay hydrated : Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Regular check-ups : Have your prostate checked regularly, especially if there are risk factors.
Conclusion
Prostate stones can cause discomfort and health problems, but with the right knowledge and treatment, these conditions can be effectively managed.