Many men experience an increase in often pee as they get older. But what often means peeing? If you drink about 1.5 to 2 liters per day, it is normal to have to pee 5 to 8 times a day. However, do you have to pee much more often and once you arrive on the toilet, you can only easily pee and produce a small amount of urine? Then we speak of often peeing. The medical term for this is Pollakisuria.
Pey problems in men can manifest themselves in various ways. The most common problems are:
1. Often peeing with the man (Pollakisuria)
Many men experience the need to pee often, both during the day and at night (nycturia). This can lead to sleep disorders and a reduced quality of life.
Often pee at night
2. Difficult peeing with the man
Difficulty peeing can manifest itself in a weak urine stream, the feeling that you have to press to start peeing or a delayed start of the urine flow. Many men notice that the power of their urine bead is reduced. This can ensure that it takes longer to empty the bladder and can cause frustration.
3. Incomplete emptying of the bladder
The feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied after urinating can lead to a constant urge to pee and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
4. Drip
After urinating, men may suffer from dripping, with some urine leaking from the urethra after they have finished peeing.
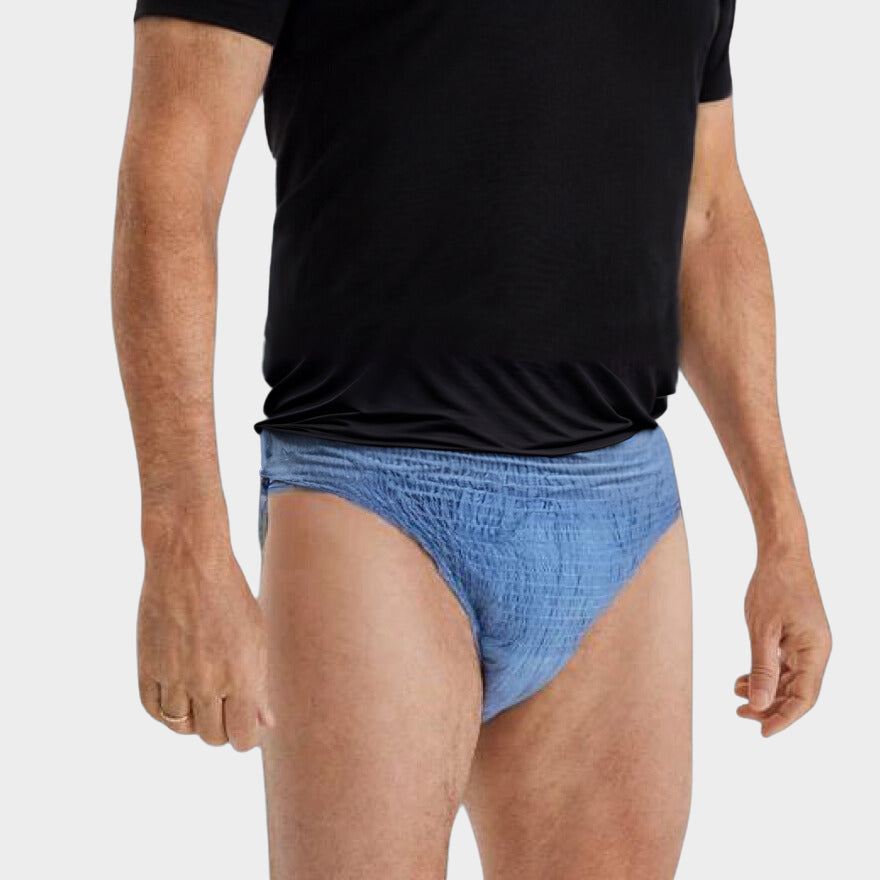
Many men experience the uncomfortable and sometimes embarrassing problem of dripping after peeing. This can not only lead to unwanted damp spots on the clothing, but also to feelings of uncertainty and discomfort. Fortunately, there are solutions available to tackle this problem. One of these solutions is the use of Antilek Underwear, such as the washable anti -leak underwear for men from Robin Underwear.
5. Intermittering peeing
This means that the urine bead stops several times and starts again while urinating, which makes the process uncomfortable and time -consuming.
What are the causes of peeing problems in men?
There are various causes of peeing problems in men, including:
1. Enlarged prostate (benign prostate hyperplasia - bph)
A enlargement Can put pressure on the urethra, leading to an obstruction of the urine flow and different urinary problems. This is a common cause in older men.
2. Prostatitis
Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate, can cause pain and difficulty peeing. It can be both acute and chronic and varies in severity.
3. Prostate cancer
Although less often, peeing problems can also be a symptom of prostate cancer. Regular checks and early detection are crucial for treatment.
4. Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
In men, UTIs can cause pain and burning sensation while urinating, as well as frequent urination and the feeling of a full bladder.
5. Bladder problems
Problems with the bladder, such as overactive bladder syndrome, can lead to frequent urination and a sudden, strong urge to pee.
Diagnostic methods for peeing problems
A correct diagnosis is essential for effective treatment of urinary problems. Some commonly used diagnostic methods are:
- Anamnesis and physical examination: The doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and perform a physical examination, including a rectal examination to assess the prostate.
- Urine examination: This can help to exclude infections and other disorders.
- Blood test: PSA tests (prostate specific antigen) can help detect prostate problems.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound and other imaging techniques can be used to assess the size and condition of the prostate and bladder.
- Urodynamic examination: This measures the pressure in the bladder and the urine flow to identify problems with the bladder and urethra.
Treatment options for peeing problems in men
The treatment of urinary problems depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Some possible treatment options are:
1. Medication
Medications can be effective for many urinary problems. Alfablokkers and 5-alpha reducture inhibitors can help with an enlarged prostate, while antibiotics may be needed for infections.
2. Minimum invasive procedures
For some prostate problems, minimally invasive procedures, such as Tumt (transurethral microwave thermotherapy) and Tuna (transurethral needle ablation), can offer a solution.
3. Surgical interventions
Surgery may be needed in more serious cases. Procedures such as TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate) can provide relief with an enlarged prostate.
4. Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing caffeine and alcohol, regular exercise and pelvic floor exercises, can help control symptoms.
5. Blaast training
Blowing training can help improve control of the bladder and reduce the frequency of urination.
When should you seek medical help?
If you suffer from pee problems that influence your daily lives, it is important to seek medical help. Timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. At Andros Clinics, experienced specialists are ready to help you with the right diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.